In automated assembly, intelligent manufacturing, and tightening systems, the screw feeding machine, as the core equipment for automatic screw feeding and conveying, directly determines tightening efficiency, assembly cycle time, and overall line stability. With the continuous improvement of industrial automation, screw feeding machines have gradually evolved from traditional auxiliary equipment to indispensable key units in the tightening process. So what exactly do screw feeding machines rely on as power sources? What technical characteristics and applicable scenarios do different structural forms of screw feeding machines have? This article provides a systematic analysis around several mainstream screw feeding machines.
I. Disc Screw Feeding Machine: Dual-Power Collaborative Solution of Motor + Vacuum Adsorption
The turntable screw feeding machine is specially designed for micro screws in the 3C industry. Its power system adopts a "motor drive + vacuum adsorption" dual-power collaborative solution, achieving stable operation of the screw feeding process through the coordination of two core power components.
Motor Drive: The motor is one of the core drive sources. Turntable screw feeding machines are typically equipped with high-precision motors featuring accurate positioning and stable operation characteristics. Through transmission mechanisms, they connect to waterwheel-type feeding structures, continuously conveying screws from the hopper to above the turntable, laying the foundation for subsequent vacuum adsorption feeding.
Vacuum Adsorption: The vacuum generator, as a pneumatic component, creates a negative pressure environment through the high-speed flow of compressed air, firmly adsorbing screws onto the turntable holes to prevent deviation or dropping during rotation. The adsorption force is controllable and can adapt to different specifications and weights of screws.

This feeding mechanism gives the turntable screw feeding machine the core advantage of "0-jam feeding," fundamentally solving the common screw congestion and jamming problems of traditional screw feeding machines. Therefore, it is highly favored in scenarios requiring high screw feeding precision, such as electronic components, precision instruments, and automotive parts.
II. Vibratory Bowl Screw Feeding Machine: Universal Solution Driven by Electromagnet Vibration
The vibratory bowl screw feeding machine is the most widely used universal model. Its power source mainly relies on the attraction force of electromagnets to generate vibration, driving screws to convey orderly along preset tracks through vibrational energy. The core power component is a high-frequency electromagnet, featuring fast response speed and stable vibration frequency, providing continuous and stable vibrational power for the feeding process.
Bowl/Hopper: Symmetrically distributed electromagnets are installed at the bottom of the hopper. When powered, they generate periodic electromagnetic attraction force, driving the hopper to perform high-frequency, small-amplitude vertical vibration. This vibrational power is transmitted to internal screws through the hopper, giving them kinetic energy to move along the track. The interior of the hopper is designed with a spiral ascending track matching screw specifications. Under the action of vibrational energy, screws ascend slowly along the spiral track and enter the linear vibration track.
Linear Vibration Track: The linear vibration track is also driven by electromagnets, driving screws forward through high-frequency reciprocating motion. Under gravity, screw shafts naturally hang down, while screw heads (with diameters larger than slot width) suspend on the track, achieving screw posture correction. Abnormal posture screws are rejected through side air-blowing mechanisms. Subsequently, the end separation mechanism separates continuously conveyed screws one by one, ensuring only one screw is conveyed to the assembly station each time.
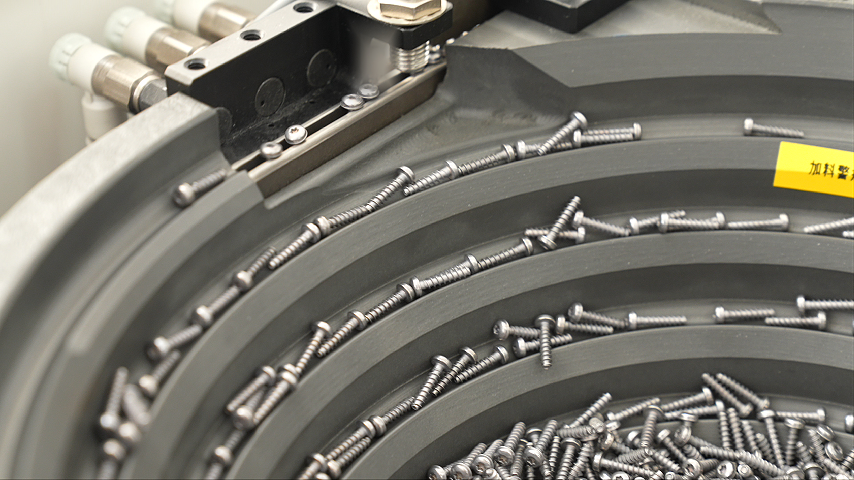

The vibratory bowl screw feeding machine features simple structure, low manufacturing cost, and convenient maintenance, widely used in automated production lines for furniture and home appliances, such as the conveying task of a large number of self-tapping screws in refrigerator and washing machine casing assembly.
III. Step-Type Screw Feeding Machine: Clean, Low-Wear Solution Driven by Cylinder
The step-type screw feeding machine focuses on cleanliness, low wear, and high stability. Its power source mainly relies on a cylinder driving a push plate to perform reciprocating motion, achieving orderly screw conveying through mechanical thrust. The cylinder, as the core power component, features stable power output, fast response speed, and smooth operation, providing continuous and controllable thrust for the push plate's reciprocating motion.
Hopper: The bottom of the hopper is inclined, utilizing gravity to make screws naturally slide to the starting position of the push plate, avoiding accumulation and jamming. The push plate adopts a step-type design, capable of pushing screws from the bottom to the linear vibration track layer by layer. Driven by the cylinder without vibration sources, it can reduce friction between screws and surface damage, achieving clean feeding.
Linear Vibration Track: The linear vibration track of the step-type screw feeding machine is the same as that of the vibratory bowl type, both driving screws to move orderly along the track through directional vibrational force generated by electromagnetic vibrators, while completing posture calibration.
The step-type screw feeding machine can meet the stringent requirements for surface quality and cleanliness in high-end product assembly such as medical devices and aerospace components. Moreover, the jamming rate for standard screws is lower than 50PPM, making operation more stable compared with the 200PPM of vibratory bowl types.
The power technologies of these three types of screw feeding machines each have their own focus, jointly forming a diversified product system in the screw feeding machine market, providing strong support for automated production in different industries. As key equipment in automated assembly lines, the innovation and upgrading of their power technologies will directly promote the improvement of manufacturing production efficiency and product quality.













